Overview
Every woman’s fertility journey is unique, but most are likely to be most fertile in the middle of their menstrual cycle. This is the time when your chances of conception are at their highest.
Your fertility will be impacted by various factors (e.g.: age, lifestyle habits). Let’s delve into these factors and understand how ovulation works to maximize your chances of getting pregnant.
The Best Time to Conceive: How Age Affects Your Pregnancy Chances
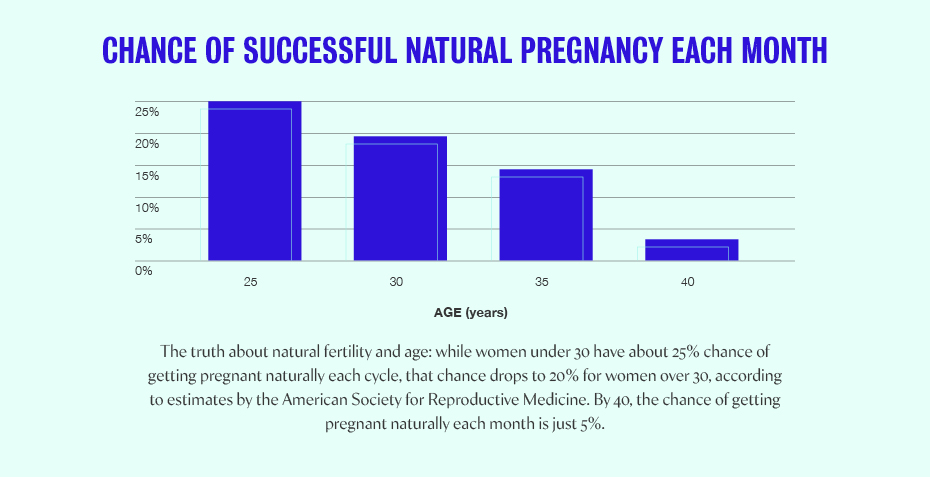
Did you know that if you’re in your early to mid-20s, you have a 25-30% chance of getting pregnant per cycle? However, the rate declines with age and can be as low as a 5% chance per cycle by the time you reach 40. (1)(2)
More and more women are choosing to become mothers later in life; it’s becoming more commonplace for women in their late 30s and early 40s to become first-time moms.
Understanding how age impacts fertility can help you make informed decisions on your journey to parenthood.
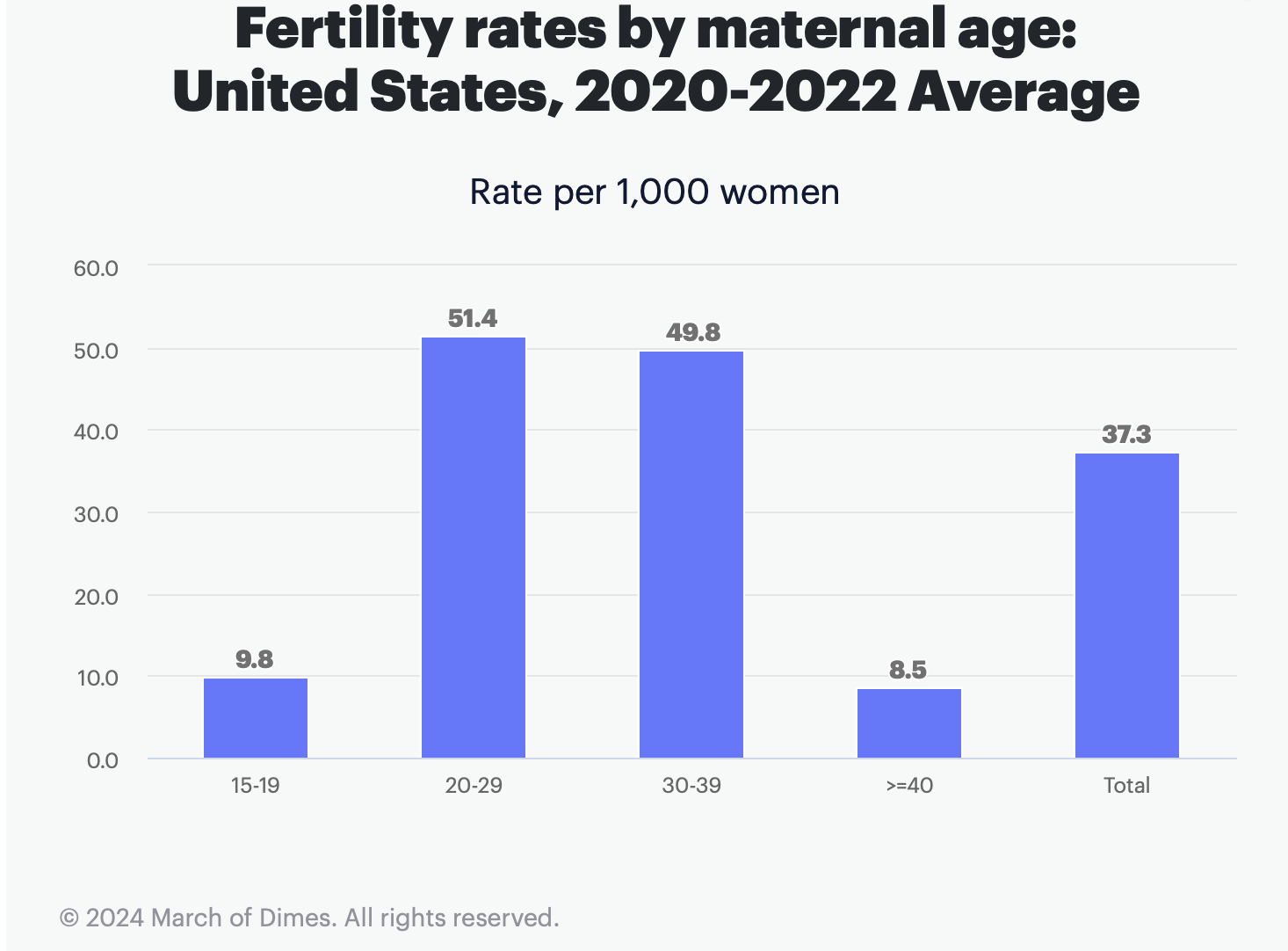
Fertility is higher during the natural ‘childbearing age range.’ Based on the table below, fertility rates are higher among women 20-39 years old than for older (40+) or younger (15-19 years old). (3)
The US Census Bureau data support these stats via the National Center for Health Statistics. Here are the US fertility rates based on maternal ages: (3)
When To Seek Medical Advice
Because fertility declines with age, it’s ideal to immediately see your healthcare provider if you’re 40+ and TTC (trying to conceive).
Younger women can follow these recommendations in seeing an OB/GYN or fertility specialist: (4)
- 35 to 39 years old – after six months of TTC
- Younger than 35 years old – after one year of TTC
With this said, it’s important to remember that you may still be able to get pregnant at an advanced age. It might just take more time and more effort on your part.
What’s Fertility?
Fertility, by definition, is a person’s ability to have a baby or conceive. It’s affected by several factors, including your age, health, habits, and lifestyle. Read more about what impacts your fertility in our in-depth article.
Your Most Fertile Days: Maximizing Your Pregnancy Chances
You have a higher chance of conceiving if you have sex within your fertility window.
Understanding The 6+1 Fertility Window
Your fertile window is just an estimate, but here’s the 6+1 fertility window estimate:
- 6 = 5 days that sperm can live in your reproductive tract + the ovulation day
- 1 = the extra day after ovulation
The rule of thumb for estimating ovulation is to subtract 14 days from your cycle length to find your ovulation day. Then, use the 6+1 fertility window to estimate your most fertile days.
Here are some examples based on different cycle lengths:
- 21 day cycle – Ovulation at day 7; most fertile at days 2 to 8
- 28 day cycle – Ovulation at day 14; most fertile at days 9 to 15
- 32 day cycle – Ovulation at day 18; most fertile at days 13 to 19
Conception is affected by many factors, including egg quality, timing, sperm availability and quality, and actual implantation. So, ovulation alone isn’t a guarantee that you’ll get pregnant. (1)
Key Facts: A Look Into Your Menstrual Cycle
Your menstrual cycle is your reproductive system’s cycle to prepare for possible pregnancy. It has four phases: (5)
- Menses Phase – Begins on the first day of your period, shedding the uterine lining if the egg wasn’t fertilized.
- Follicular Phase – Also starts on the first day of your period (overlaps with the menses phase); your body prepares for ovulation by increasing estrogen production, thickening your endometrium (lining of your uterus), and producing FSH ( follicle-stimulating hormone) to grow follicles into a mature egg
- Ovulation Phase – Occurs at around day 14 for a 28-day cycle; begins on the day of ovulation when your body releases more LH (luteinizing hormone), signaling the ovary to release the mature egg
- Luteal Phase – The mature egg is ready for fertilization and slowly travels through the fallopian tube while your body produces more progesterone to increase your chance of implantation if it is fertilized; if the egg isn’t fertilized, progesterone and estrogen hormone levels drop, then the thickened uterine lining is shed off as your period starts (new menstrual cycle)
What’s The Average Menstrual Cycle Length?
Menstrual cycle length varies among women but typically lasts between 24 and 35 days. Many women go through a 28-day cycle. (5)
Women with irregular cycles don’t follow a specific pattern and might ‘skip’ periods for one or more months. (5)
What Is Ovulation & How Does It Happen?
Ovulation is the moment a mature egg is released from your ovary. It happens soon after your body releases a high level of luteinizing hormone, the hormone checked by ovulation test kits. (5)
How Long Does Ovulation Take?
The egg release itself happens within just a day, but the preparation for egg maturation is around 14 days for an average cycle of 28 days. Your actual ovulation day depends on the length of your menstrual cycle. (5)
How Does Conception Happen?
Conception (the union of the matured egg with sperm) happens along the fallopian tubes, usually close to the ovary. Your chance of pregnancy is higher if you have sex closer to the time of ovulation. (1)(2)
The good news is that motile (active) sperm can live up to five days along your reproductive tract. So, it’s still possible to conceive even if you didn’t have sex on ovulation day, as long as active sperm is available. (6)
How Many Days After Your Period Are The Most Fertile?
The matured egg can only be fertilized within 12-24 hours after release. This chance rapidly decreases if it doesn’t meet and unite with any sperm within your fertile time. (5)(6)
So, you’re the most fertile on your ovulation day.
What Are The Three Most Fertile Days?
- One day before ovulation
- Ovulation day
- One day after ovulation
How Many Days After Your Last Period Can You Get Pregnant?
You can actually get pregnant by having sex anytime during your cycle, even outside your most fertile window. However, your chances of pregnancy are low. (6)
Still, always remember that sperm can live up to about five days in your reproductive tract, and ovulation might happen earlier or later than scheduled. Keep these in mind, especially if you’re trying to avoid pregnancy with natural family planning methods (hint: it isn’t fail-proof). (6)
What’s A Period Or Menstruation & Why Does It Happen?
Menstruation, or the menstrual period, is the blood released from the uterine lining when an egg isn’t fertilized or the fertilized egg didn’t successfully implant in your uterus. It signals the start of a new menstrual cycle. (5)
A regular period usually lasts 3-7 days. (5)
All About Timing: How Do You Know You’re Ovulating & Fertile?
Do You Need Special Tools To Know You’re Ovulating?
You don’t always need to get special tools to check for signs of ovulation. Some signs to look out for without spending a dime: (discussed below) (7)
- Ovulation date using the calendar method (only works for regular cycles)
- Cervical mucus
- Basal body temperature
Still, tracking your ovulation using special tools (e.g., an ovulation predictor kit or a phone tracker app) can be easier.
Calculating & Estimating Your Ovulation Day
Using An Ovulation Calculator & Calendar Method (Regular Or Irregular Periods)
Track your menstrual cycle using a calendar by plotting the first day of your period. This requires at least a few months of tracking but will help you determine the number of days your typical menstrual cycle lasts.
Here’s a guide to using the calendar method, according to Christine Curley Skiadas, MD, of Penn Medicine’s Lancaster General Health: (7)
- Subtract 18 days from your shortest recorded cycle. Add this number to the first day of your next menstrual cycle, and put an X on the calendar.
- Subtract 11 days from your longest recorded cycle. Add this number to the first day of your next menstrual cycle, and put an X on the calendar.
- Ovulation might happen between the days marked by the two Xs.
Using An Ovulation App Or Tracker
Dr. Skiadas also recommends using ovulation apps to track your cycle. (7)
Here are some of the most common ovulation tracker apps:
Some popular examples include:
- Flo – Tracks period and ovulation cycles; also includes personalized insights based on your data input
- Clue – Tracks menstrual cycles, energy levels, emotions, etc.
- Period Tracker – Tracks periods, ovulation dates, fertility, and symptoms; also includes community support
- Ovia Fertility & Cycle Tracker – Personalized fertility predictions and cycle tracking; also includes health insights and tips
- Glow – Tracks periods, ovulation, and possible fertile dates; also includes reports or insights based on data input and has community forums
- My Cycles – Tracks menstrual cycles, fertility windows, ovulation, and symptoms; also includes health insights
Your Body’s Top Signs That You’re Ovulating (Or About To)
Checking Your Vaginal & Cervical Mucus Changes
Hormonal changes within the menstrual cycle can affect how your cervical mucus or vaginal discharge appears. (7)(8)
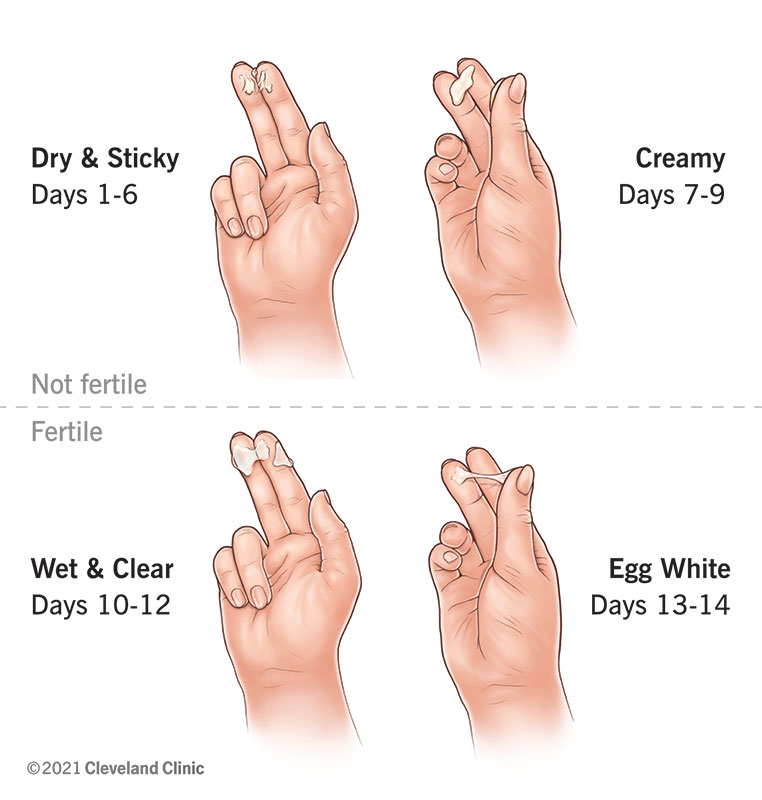
During the first few days of your menstrual cycle (days 1-6), your cervical mucus can be described as “dry.” It becomes “creamy” around days 7-9 as your egg matures. You’re likely not fertile during these days. (7)(8)
By days 10-12, your cervical mucus becomes wet and clear. This can already signal your fertile window, with the mucus becoming more ‘sperm-friendly.’ During ovulation, your cervical mucus becomes similar in consistency to egg whites. (7)(8)
Monitoring Your Basal Body Temperature
Similar to the calendar method, this requires regular monitoring. Track your body temperature the moment you wake up, even before getting up from bed or peeing. (7)
A rise of around 0.4 or 0.8 degrees Fahrenheit might signal that you’re ovulating. This can happen on the day of ovulation or as a gradual increase before the day arrives. (7)
Using An Ovulation Predictor Kit
Ovulation predictor kits test for the presence of luteinizing hormone. The hormone triggers ovulation, so higher levels in your blood can mean that you’re ovulating or about to ovulate. (7)
Start testing on day 10 or 11 if you have a regular 28-day cycle. If you have irregular cycles, begin testing using the number of days in the middle of your shortest cycle. (7)
Some ovulation test kits to try:
- Clearblue Advanced Ovulation Test
- Easy@Home 50 Ovulation Test Strips
- Pregmate 50 Ovulation Test Strips & Predictor Kit
Other Possible Fertility Signs
Mood Changes
Some women experience mood swings close to or on the day of ovulation. It doesn’t happen to everyone and might not even happen every month for those who experience it. (9)
You might consider creating a period symptom diary to monitor other things you experience during your menstrual cycle. It might also help you discover subtle ovulation signs. (9)
Discomfort Or Abdominal Pain
Also called Mittelschmerz, this one-sided lower abdominal pain is associated with ovulation and happens around day 14 of your menstrual cycle (for regular cycles). It rarely requires medical attention but might last a few hours or days. (9)(10)
Changes In Your Libido
Getting pregnant is your body’s natural goal during ovulation. So, you might also experience increased libido during your fertile window. However, it might not happen every month. (9)(11)
Clearer & Brighter Skin Or Acne Breakouts
It’s different for every woman. Some might experience brighter and clearer skin, while others have an acne breakout. All of these are due to hormonal imbalances or changes during ovulation. (11)
Other Ovulation Signs & Pains
Some women also experience the following close to ovulation day: (9)(11)
- Nausea
- Bloating
- Breast tenderness
- Headaches
It’s also okay if you don’t experience any of the ovulation signs we’ve mentioned above. Some women don’t show these signs, and that’s normal too. If this is you, consider using ovulation test kits or other methods to monitor your menstrual cycle.
Can You Use Ovulation Trackers Or Predictors With PCOS?
Sometimes, yes. Although PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) can lead to irregular cycles, you might still use the methods above for ovulation prediction, especially the ovulation test kits. Note, however, that periods are often irregular or absent with PCOS – and having regular periods doesn’t always mean you’re ovulating every month. (9)
Factors That Might Affect Your Ovulation & Pregnancy Chances
Possible reasons for female infertility: (12)(13)
- Conditions affecting the uterus (e.g., uterine polyps, fibroids, etc.)
- Endometriosis (uterine tissue growth outside the uterus)
- Fallopian tube damage or problems
- Pelvic adhesions (scars that bind parts of your reproductive system together)
- Ovulation disorders, e.g., PCOS, LUFS (luteinized unruptured follicle syndrome), and (amenorrhea or no period for 3+ months)
- Cancer and treatments
Possible reasons for male infertility: (14)(15)
- Low or insufficient sperm count
- Low or inefficient sperm motility (movement)
- Different sperm morphology (size and shape)
- Reproductive system problems such as varicoceles (enlarged veins in their scrotum), which can lead to poor testicular development, possibly low sperm production, and other infertility issues
Learn more about male and female fertility and infertility (plus their treatment or management options) in our article.
Increasing Your Chances Of Getting Pregnant
Regular Vs. Timed: When’s The Best Time To Have Sex To Get Pregnant?
Depending on your ovulation and fertility window, your doctor might recommend daily (regular) or timed sexual intercourse (closest to your most fertile days).
Regular sex can provide your reproductive tract with readily available sperm that might fertilize the egg anytime it is released. However, sperm health and motility aren’t guaranteed, so it’s still possible you won’t get pregnant.
Timed sex ensures freshly available sperm during your fertility window. However, as previously explained, this doesn’t carry a 100% guarantee of getting pregnant.
Other Ways To Increase Your Pregnancy Chances
- Manage stress
- Limit caffeine and alcohol intake
- Avoid smoking and recreational drugs
- Improve your health & manage medical conditions
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Address vitamin and mineral insufficiency or excess
- Keep systemic bodily inflammation low
- Get a consistent 7-8 hours of quality sleep nightly
- Acupuncture and herbs
- Castor oil packs
- Addressing unresolved trauma
Busting Some Fertility Myths
Myth: You Need To Have Sex Everyday To Get Pregnant
No. Only one sperm is needed to fertilize the released egg. Because sperm can survive up to five days, then even just one sexual contact can lead to pregnancy. (16)(17)
Myth: You Can Get Pregnant Anytime During Your Cycle
Well, technically, it can still happen because sperm can survive for five days, and you might have a longer or shorter cycle. However, pregnancy chances outside your fertile window are low. (16)(17)
According to the ACOG (American College Of Obstetricians And Gynecologists), if done correctly, fertility awareness can be an effective natural family planning method, with fewer than 1-5 out of 100 women getting pregnant during the first year of “perfect use” (using the method correctly and consistently). (16)
Fertility awareness includes: (16)
- Calendar method
- Cervical mucus method
- Basal body temperature method
- Symptothermal method (combination of temperature plus other methods)
Myth: You Can’t Get Pregnant On Your Period
It’s unlikely, but you can still get pregnant even if you have sex on your period. Again, that depends on certain factors, such as the actual date of intercourse (e.g., the seventh day of your period) and sperm survival, which might be closer to your ovulation day (for shorter cycles). (16)(17)
What If You Want To Avoid Getting Pregnant?
When Are You Least Likely To Get Pregnant?
Your chances of getting pregnant decrease around 2+ days (or at least 36 to 48 hours) after ovulation until your next period. (17)
You’re Less Likely To Get Pregnant Two Days Before Your Next Period
The further after ovulation, the less likely you’ll become pregnant. (17)
Can You Still Get Pregnant During Sex Without Penetration?
It’s unlikely, but if sperm comes in contact with your vagina, it might still be strong enough to swim up to your fallopian tubes and fertilize an available egg. (18)
How Do Contraceptive Pills Work?
Also called birth control pills, contraceptive pills prevent pregnancy by ensuring your body can’t support a pregnancy: (19)
- Prevents ovulation
- Thins your uterine lining to prevent implantation
- Thickens your cervical mucus to create a physical barrier that blocks semen/sperm from reaching the egg
When Does Your Fertility Return After Pregnancy & Childbirth?
It’s different for every woman. Some might already release an egg about a month after childbirth, though others need around six months before fertility returns. Breastfeeding can delay fertility return but doesn’t guarantee it. (20)
Talk to your OB/GYN about birth control methods, especially if you’re breastfeeding.
When Should You Start Preparing For Preconception Health & Prenatal Visits?
You can start as soon as possible without waiting for your next period. After all, your chances of pregnancy can increase if you’re healthy. Seek medical advice from your OB/GYN, though you can also talk to any healthcare professional outside the obstetrics/gynecology department.
Other Things To Do To Prepare For Pregnancy
- Take prenatal vitamins
- Take folate, iron, iodine, choline, fish oil, and other supplements
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Start a regular exercise regimen (e.g., prenatal yoga)
- Make sure your vaccinations are updated
- Get treatment for your medical concerns (e.g., chronic hypertension)
References
(1) https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/age-and-fertility#
(2) https://extendfertility.com/your-fertility-3/fertility-and-age/
(3) https://www.marchofdimes.org/peristats/data?reg=99&top=2&stop=2&lev=1&slev=1&obj=1
(4) https://healthcare.utah.edu/fertility/when-should-you-see-a-fertility-specialist
(5) https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/10132-menstrual-cycle
(6) https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/conception-how-it-works
(7) https://www.lancastergeneralhealth.org/health-hub-home/2022/november/how-ovulation-prediction-tools-can-help-you-get-pregnant
(8) https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21957-cervical-mucus
(9) https://fertilityfoundation.org/ovulation-symptoms-signs-of-ovulation/
(10) https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/mittelschmerz/symptoms-causes/syc-20375122
(11) https://www.tuasaude.com/en/ovulation-symptoms/
(12) https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/infertility/symptoms-causes/syc-20354317
(13) https://lomalindafertility.com/pregnancy/menstrual-cycle/
(14) https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/m/male-infertility
(15) https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/varicocele/symptoms-causes/syc-20378771
(16) https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/fertility-awareness-based-methods-of-family-planning
(17) https://americanpregnancy.org/can-i-get-pregnant-if/can-you-get-pregnant-on-your-period/
(18) https://www.tuasaude.com/en/how-can-you-get-pregnant-without-penetration/
(19) https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/3977-birth-control-the-pill
(20) https://www2.hse.ie/babies-children/breastfeeding/fertility-other-children/fertility/