Overview
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun are important for vitamin D production, yet overexposure can also be harmful. It can lead to sunburn, eye damage, skin aging (e.g., “leathery skin” and wrinkles), and might cause skin cancer. (1)
Data from the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) show that around 6.1 million people receive treatment for skin cancer each year in the US. (2)
And the US National Cancer Institute warns that skin cancer is on the rise, with around 99,780 new cases and 7,650 related deaths in 2022. (3)
Babies and young children are especially vulnerable because of their still-developing bodies and protective systems. These make them potentially more susceptive to the carcinogenic effects of UV radiation. (4)
Your young children depend on you as their parent to provide them with protective measures from the sun.
A lack of skin protection not only increases your children’s risks of developing skin cancer but can also lead to painful sunburns and skin damage.
What’s the safe UV level for babies, and how can you protect them from the harmful effects of the sun’s rays? Get answers to your questions below.
Is It Okay To Expose My Baby To Sunlight?
Yes – but only for a limited time, with sun protection (e.g., sunblock lotion), and depending on the UV index (see below).
However, be sure to consult with your pediatrician before using sunscreen or sunblock on babies who are younger than six months. (3)
It’s also important to ensure that while applying sun protection liberally on exposed skin areas, avoid putting it close to your baby’s eyes and mouth. (3)
Healthcare providers usually suggest sunlight exposure during the early morning or late afternoon hours if that isn’t feasible.
The FDA also recommends limiting sun exposure, especially around noon (10 AM to 2 PM), because the sun’s rays are more intense during these hours. (3)
How Does UV Exposure Affect People & Babies?
Based on data from the CDC, skin cancer rates are higher in adults than in children. However, these are mainly due to adults getting more sun exposure than younger children and babies. (5)*
*NOTE: The reference link leads to a general demographics list. Set the cancer type to “melanomas of the skin” to find relevant data on this webpage.
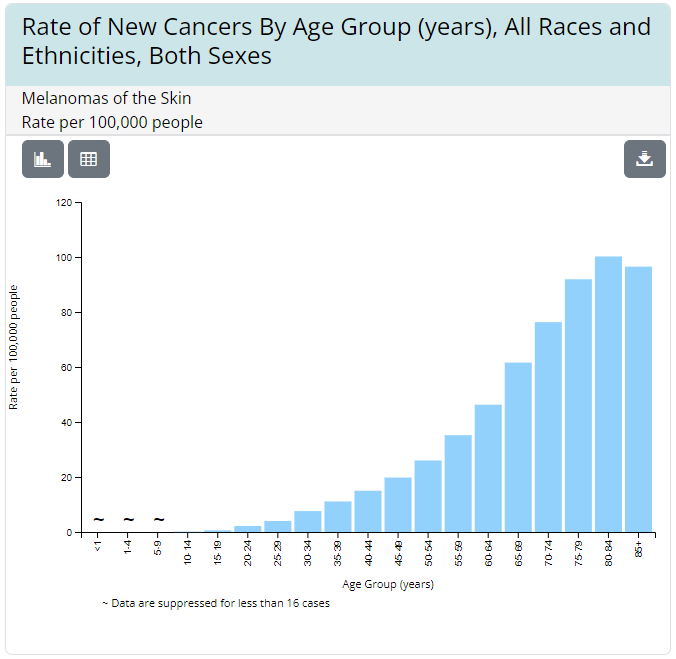
(source: gis.cdc.gov)
It’s also important to note that fair-skinned people may be more susceptible to skin cancer than those with darker skin (see chart below).
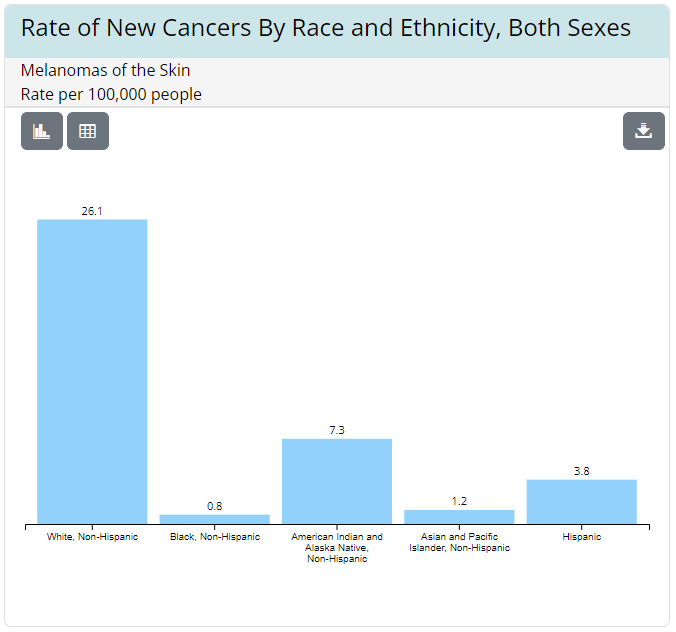 (source: gis.cdc.gov)
(source: gis.cdc.gov)
Why Are Babies At Risk For Skin Cancer From Overexposure To The Sun?
Although the number of children with skin cancer is significantly lower than adults (based on the data above), this younger population is still considered vulnerable and at risk.
Some of the reasons why babies and young children are at risk for skin cancer: (4)
- Their bodies are still developing (e.g., their skin is thinner). This means that their skin might not provide enough protection from the sun and can burn easily.
- Their protective systems aren’t fully developed, making their bodies vulnerable to the carcinogenic effects of UV radiation.
- They have a higher skin-to-body-mass ratio than adults, so sunburns and other ill effects of overexposure to UV rays can be more serious.
- They depend on you to protect them from the sun.
- They can’t communicate as well as adults, so you might not realize they’re crying because their skin or body has become too hot or burned.
- They might not be able to move out of the sun and find shelter (or they are unlikely to understand that sunlight exposure makes their bodies and skin hot).
What Level Of UV Is Safe For Babies?
Safe UV levels for babies and people are between 0 to 2 (according to the UV index scale). (6)
The US uses a UV index scale established by the WHO (World Health Organization). Here’s a guide to reading the scale and what to do to keep your baby safe: (6)
- 0-2 (low UV) – Possibly safe to stay outdoors with minimal sun protection (limit sun exposure of babies 0-6 months old; regularly check the temperature of babies 6+ months old)
- 3-7 (moderate to high UV) – Seek shade; requires protection (e.g., sunglasses, broad-spectrum SPF-15 or higher sunscreen, protective clothing, etc.)
- 8+ (very high to extreme UV) – Requires extra protection (e.g., generously apply broad-spectrum SPF-15 or higher sunscreen, at least UPF 50 or ultraviolet protection factor 50 clothing, sunglasses, a wide-brimmed hat, etc.)
If possible, avoid exposing your baby to the sun when the UV index is 8+ in your area.
You can check the daily forecast (via epa.gov/sunsafety/uv-index-1) or your local weather bureau.
Here are some recent examples of the UV indices in the US at solar noon hours:
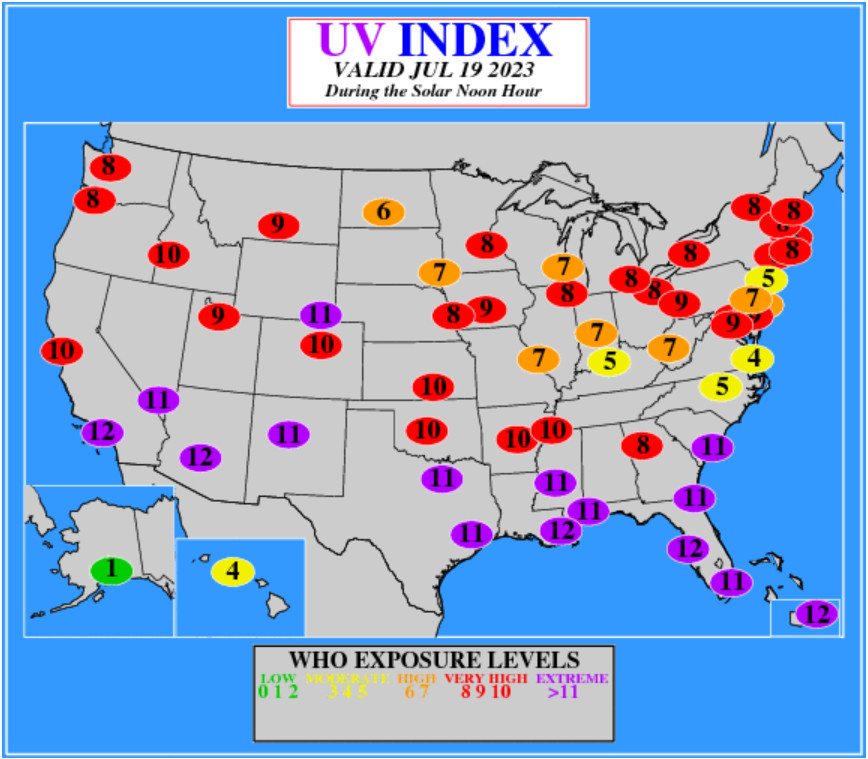 (source: epa.gov)
(source: epa.gov)
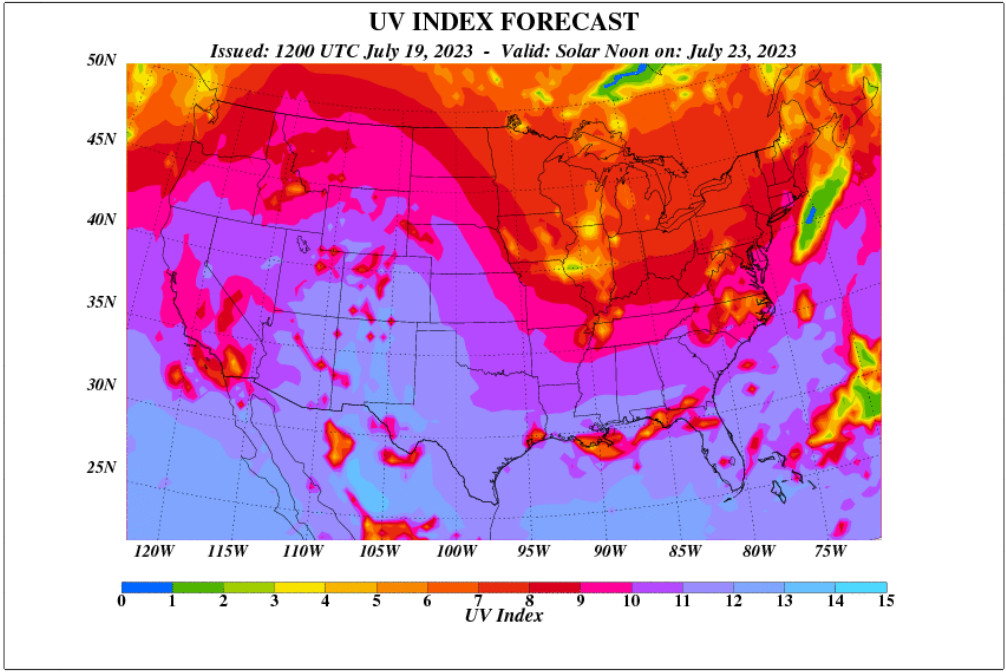 (source: epa.gov)
(source: epa.gov)
Can Children’s Sunburn Increase Cancer Risks?
Yes. It’s important to avoid sunburn because it can have long-term effects on children, including cancer risks, even when the skin appears to have healed. (7)
Intermountain Riverton Hospital Dermatologist Dylan Alston, DO, in Riverton, Utah, explains: (7)
“A sunburn before age one more than doubles your risk of melanoma. Short-term, high-intensity sun exposure during childhood poses the greatest risk for getting skin cancer later.”
“But more importantly, sunburns in babies can be a medical emergency that causes dehydration, fevers, blisters, and even heatstroke.”
How Do You Shield A Baby From The Sun & UV Rays?
Below are some ideas to protect your baby from the sun based on age.
Note: The sun has two types of UV rays: UV-A penetrates deeper and can be responsible for skin cancer and premature aging, while UV-B damages the surface and can cause sunburns.
Most sunscreens protect from UV-B rays, while sunblock protects from both.
0-6 Months Old
- Don’t use sunscreen or sunblock. Babies younger than six months have sensitive skin, and their bodies can’t metabolize (process) and excrete the chemicals that might be in these products.
- If possible, keep your baby out of direct sunlight and keep sun exposure before 10 AM or after 4 PM.
- Use umbrellas, strollers, and infant car seats with sunshades or canopies.
- Add removable sun shields or mesh screens to car windows. UV window film can also work (but check with local regulations on tint/darkness limits).
- It’s best to choose clothing with at least UPF 50 (ultraviolet protection factor 50) because it can block 98% of the sun’s UV rays.
6+ Months Old
- Apply child-safe sunscreen or sunblock (at least SPF 30; sun protection factor) on exposed parts, and be sure to keep it away from their eyes and mouth.
- Apply it for around 30 minutes before heading outside. Reapply after excessive sweating, swimming, or every two hours (whichever comes first).
- If possible, keep sun exposure to a minimum, especially when the UV index is higher.
- It’s still best to use clothing and canopies (for strollers and bassinets) with UPF 50+.
- Introduce your child to sunglasses and hats (but be sure to check for possible choking or strangulation risks). Choose products that offer UV protection.
Toddlers & Older
- Follow the tips listed for 6+-month-old babies above.
- You can also let your toddler pick their sunglasses (make sure the choices offer UV protection) to better encourage them to wear a pair.
- If possible, use a pop-up tent, umbrella, or other extra protection for your toddler during outdoor play.
Important: Some children might experience an allergic reaction to sunscreen ingredients. Always choose a hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and child-safe product.
Even the safest-formulated products might still trigger an allergic reaction. You can check by applying a small amount to your baby’s skin. Wait for around 30 minutes and check for any sign of irritation, itching, hives, redness, or swelling.
Our Recommendations
Here are some clean, non-toxic mineral sunscreen options we recommend:
Babo Botanicals – SPF 50 Baby Face Mineral Sunscreen Stick




Pipette Mineral Sunscreen – SPF 50 Broad Spectrum Baby Sunblock (contains non-nano zinc)




Badger Baby Mineral Sunscreen Cream – SPF 40 (an organic toddler sunscreen with zinc oxide)
Babyganics – SPF 50 Kids Sunscreen Lotion (with UVA and UVB protection)
You can also find more information about vitamin D drops for your baby in our article.
References
(1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3709783/
(2) https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/skin/statistics/index.htm
(3) https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/tips-stay-safe-sun-sunscreen-sunglasses
(4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5796497/
(5) https://gis.cdc.gov/Cancer/USCS/#/Demographics/
(6) https://www.epa.gov/sunsafety/uv-index-scale-0
(7) https://intermountainhealthcare.org/blogs/topics/pediatrics/2018/05/better-than-sunscreen-dress-your-kids-in-uv-protective-clothing/